Volcano That Has Not Erupted for at Least 10 000 Years but May Erupt Again
A volcano is a land-form, a mountain, where molten rocks erupt through the surface of the planet. The volcano mountain opens downwards to a puddle of molten rocks below the surface of the earth.
When the pressure builds up in the earth's crust, eruptions occur. Gasses and rock shoots up through the opening and spill over or fill the air with lava fragments. The volcano eruption can cause lateral blasts, hot ash and lava flow, mud-slides, and more.

Categories of Volcanoes
Volcanoes are categorized into three main categories:
- Agile
- Dormant
- Extinct
An active volcano is i which is recently erupted and there is a possibility that it may erupt soon.
A fallow volcano is one that has non erupted in a long time but in that location is a possibility it can erupt in the time to come.
An extinct volcano is ane which has erupted thousands of years ago and there's no possibility of an eruption.
Types of Volcanoes
Volcanoes are grouped into four types:
- Cinder cones
- Composite volcanoes
- Shield volcanoes
- Lava volcanoes
Cinder Cones
Cinder cones are circular or oval cones made up of small fragments of lava from a single vent that take been diddled up. Cinder cones consequence from eruptions of mostly pocket-sized pieces of scoria and pyroclastics that build up around the vent.
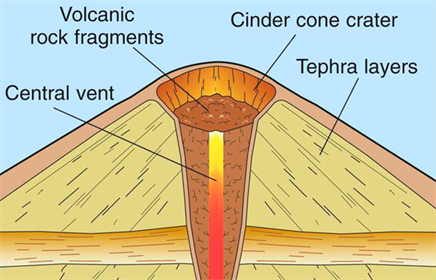
Most cinder cones erupt just once. Cinder cones may grade as flank vents on larger volcanoes, or occur on their ain.
Composite Volcano
Composite volcanoes are steep-sided volcanoes equanimous of many layers of volcanic rocks, usually made from high-viscosity lava, ash and rock debris. These types of volcanoes are tall conical mountains composed of lava flows and other ejecta in alternate layers, the strata that give ascent to the name.
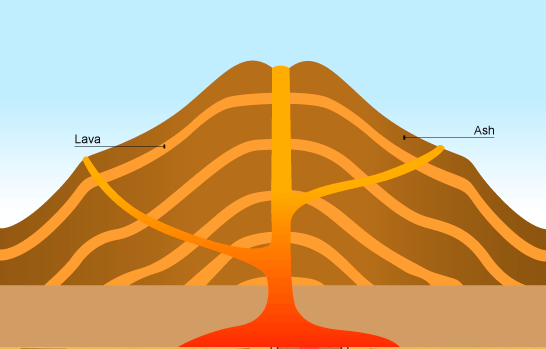
Composite volcanoes are made of cinders, ash, and lava. Cinders and ash pile on top of each other, lava flows on top of the ash, where it cools and hardens, and and so the procedure repeats.
Read More: Blended Volcano
Shield Volcano
Shield volcanoes are volcanoes shaped similar a bowl or shield in the middle with long gentle slopes made past basaltic lava flows. These are formed by the eruption of low-viscosity lava that can catamenia a great distance from a vent.
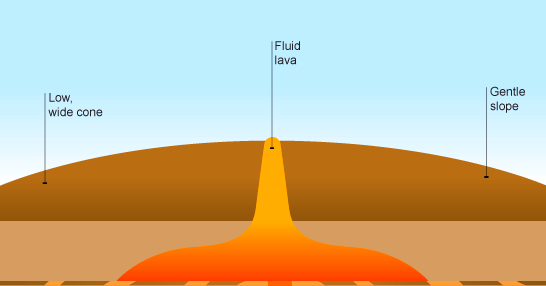
They by and large exercise not explode catastrophically. Since low-viscosity magma is typically depression in silica, shield volcanoes are more mutual in oceanic than continental settings. The Hawaiian volcanic concatenation is a serial of shield cones, and they are mutual in Iceland, also.
Read More than: Shield Volcano
Lava Domes
Lava domes are formed when erupting lava is too thick to flow and makes a steep-sided mound as the lava piles up near the volcanic vent. They are congenital past wearisome eruptions of highly gummy lava.
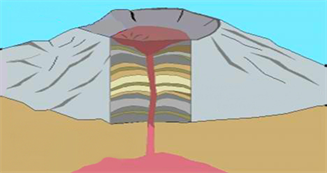
They are sometimes formed inside the crater of a previous volcanic eruption. Similar a composite volcano, they tin can produce violent, explosive eruptions, but their lava generally does not menstruation far from the originating vent.
Types of Volcanic Eruptions
Types of volcanic eruptions depend on various factors such as chemical science of magma, temperature, viscosity, volume, presence of groundwater, and water and gas content.
Following are the unlike types of volcanic eruptions:
- Hydrothermal eruption: These eruptions include ash and not magma. They are driven by the estrus caused in hydrothermal systems.
- Phreatic eruption: This is driven when the heat of the magma interacts with the water. These eruptions to practice not include magma and just ash.
- Phreatomagmatic eruption: This eruption takes identify when there is the interaction betwixt the newly formed magma and water.
- Strombolian and Hawaiian eruption: Hawaiian eruption has burn fountains while the Strombolian eruption has explosions due to lava fragments.
- Vulcanian eruption: These eruptions final for a brusque period of time and can attain upwardly to a height of 20 km.
- Subplinian and Phinian eruptions: Subplinian eruptions accomplish up to 20 km height, while Plinian eruptions reach upwardly to 20-35 km.

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Where are the most agile volcanoes?
The nearly active volcano in the earth is found in Kilauea volcano in Hawaii. Other most agile volcanoes are Etna in Italia and Piton de la Fournaise on La Reunion island.
What are volcanic rocks?
Volcanic rocks are the igneous rock that is plant in the volcanic regions. They are fine-grained, glassy textured rocks. These rocks are also vesicular in texture which is in the course of voids that are created by the volatiles that attempt to escape from the molten lava. The volcanic rocks are named based on their chemical composition. The most mutual volcanic stone is basalt. The silica content in the basalt rock is very depression. Rhyolite is a volcanic stone that has the highest silica content.
What is the relationship between volcanoes and geysers?
The human relationship between volcanoes and geysers is that both of them are dependent on the stiff heat source which is nowadays in the hush-hush. The machinery of a geyser is based on the surface miracle. When the groundwater beneath the shallow surface gets heated up, the surface explodes resulting in the boiling and steaming of the water. These surfaces become refilled once more and the cycle continues. The difference between geysers and volcanoes is that geysers usually occur in volcanic regions while volcanoes don't have geysers around them.
How volcanoes are formed?
When the magma from the earth's upper drapery erupts upwards, volcanoes are formed. When the volcano erupts at that place is a formation of lava and ashes. The lava flows downwards depositing the ashes. This cycle continues making the site bigger and bigger.
What is plate tectonics?
Plate tectonics describes the way in which the continents migrate from one some other and course a new place. When the plates motion, they collide with each other and grind each other. The tectonic movement is related to the earth's crust and upper mantle. Earthquakes are the issue of tectonic movements.
mcbridetrailtandes.blogspot.com
Source: https://byjus.com/physics/types-of-volcanoes/
0 Response to "Volcano That Has Not Erupted for at Least 10 000 Years but May Erupt Again"
Post a Comment